SoftMaxGradual approach of a floor below which output can never fall |
|
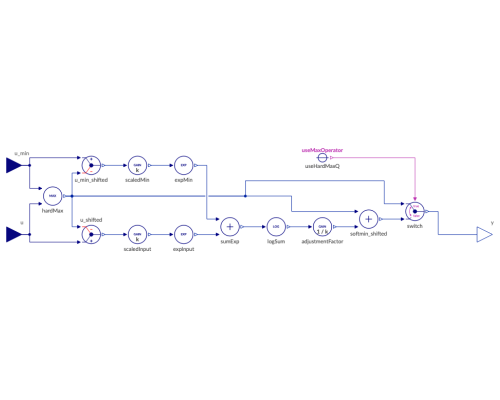
Diagram
Information
The output y is obtained as a smooth maximum with regard to the inputs u and u_min:
The following graph shows the results for u_min = 1.0 and k ∈ {10,5,3,2}:
Notes
- The soft maximum is a special case of the generalized f-mean.
See also
Parameters (2)
| k |
Value: 4.7 Type: Real Description: Parameter to control the closeness to a hard maximum |
|---|---|
| useMaxOperator |
Value: false Type: Boolean Description: = true, if a regular 'hard' maximum is to be used |
Connectors (3)
| y |
Type: RealOutput Description: Output signal |
|
|---|---|---|
| u |
Type: RealInput Description: Input |
|
| u_min |
Type: RealInput Description: The floor |
Components (13)
| u_min_shifted |
Type: Gap Description: Compare goal (u1) and current value (u2) to determine gap |
|
|---|---|---|
| u_shifted |
Type: Gap Description: Compare goal (u1) and current value (u2) to determine gap |
|
| switch |
Type: Switch Description: Switching between inputs depending upon condition |
|
| useHardMaxQ |
Type: ConstantConverterBoolean Description: A constant boolean value is turned into a constant signal |
|
| softmin_shifted |
Type: Add_2 Description: Sum of two inputs |
|
| hardMax |
Type: Max Description: Hard max operator |
|
| scaledInput |
Type: Gain Description: Input is multiplied by constant parameter |
|
| expInput |
Type: Exp Description: Natural exponential function |
|
| sumExp |
Type: Add_2 Description: Sum of two inputs |
|
| logSum |
Type: Log Description: Logarithm of the input to a given base |
|
| adjustmentFactor |
Type: Gain Description: Input is multiplied by constant parameter |
|
| expMin |
Type: Exp Description: Natural exponential function |
|
| scaledMin |
Type: Gain Description: Input is multiplied by constant parameter |
Revisions
- Introduced in v2.0.0.
- Fixed
hardMaxand numerical stability issues in v2.1.0.